Remembering passwords can be difficult considering the number of passwords we encounter in our every day lives. So, we often tend to forget one or the other every now and then. And you are in for a rough ride in case the password you forgot was your Windows password.
If you are using a Microsoft account, there is still a simple way to recover that forgotten Windows password. But the case is not so easy when it comes to local accounts in your Windows PC. However, there are a number of free and paid tools available that can provide you some relief by recovering that Windows password. Here are the top 8 tools that helps in password recovery for a Windows PC along with my views on them, which includes their pros and cons. Hope this helps you in your time of need to make the right choice of selecting the best Windows password recovery tool that is prefect for your requirement.
|
WinPassGo from SYSGeeker is a simple to use utility that helps you reset your Windows forgotten password. This utility, as per their website, has shown an impressionable success rate of 98%. What’s more, this is a GUI-based utility, so you will not have to go through the nuances of typing tedious and cryptic commands on a Command Prompt. We know all account info are stored in a SAM file which is a very difficult to obtain, but WinPassGo can be able to quickly locate the SAM file and modify it to achieve the purpose of removing the password. WinPassGo works on almost all modern versions of Windows including server/XP/7/8/10 and Widows servers. You will not need to reinstall Windows when you are using this utility, so that is virtually no chance for any loss of data.
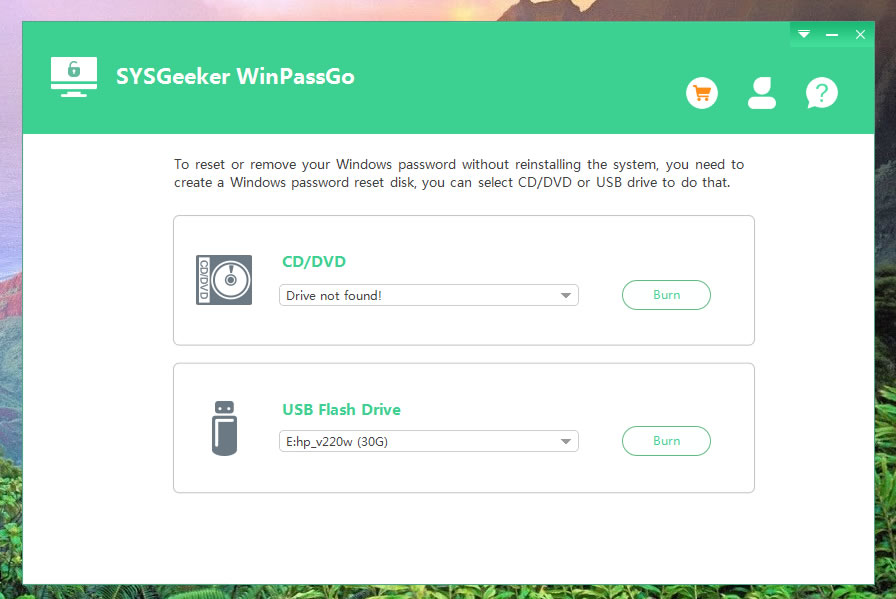
This password recovery tool functions by creating a password reset disk. Although you can use an USB drive instead of a CD/DVD in case your PC supports booting from USB. In that respect, WinPassGo supports various models and types of USB drives, CD/DVD, SSDs, pen drives etc. It also extends supports for most brand of computers including HP, DELL, IBM, Sony etc with UEFI and MRB boot modes. Once created, the password reset disk can be used multiple times, it does not really have an expiration date. You can not only recover Windows password using this utility, but also create and delete accounts on your Windows PC with ease.
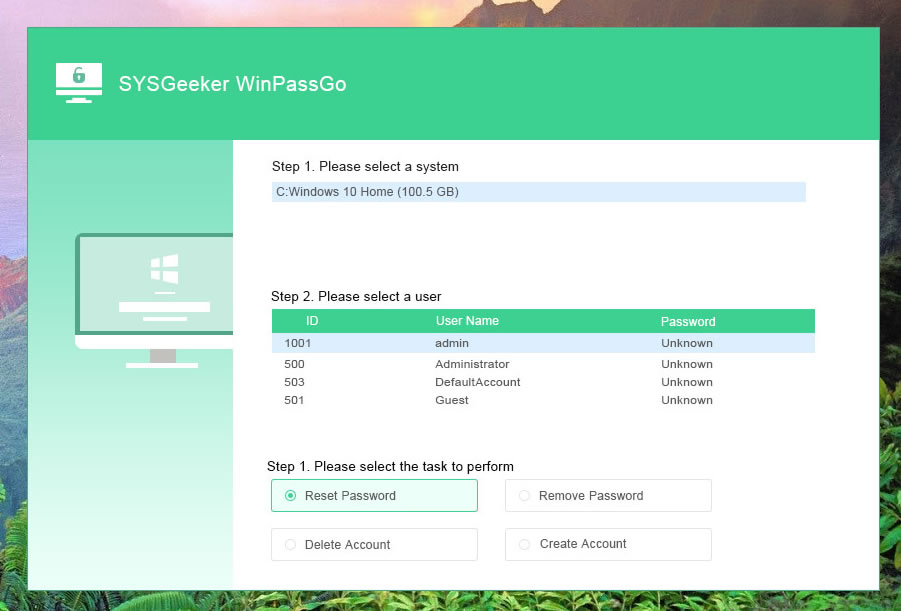
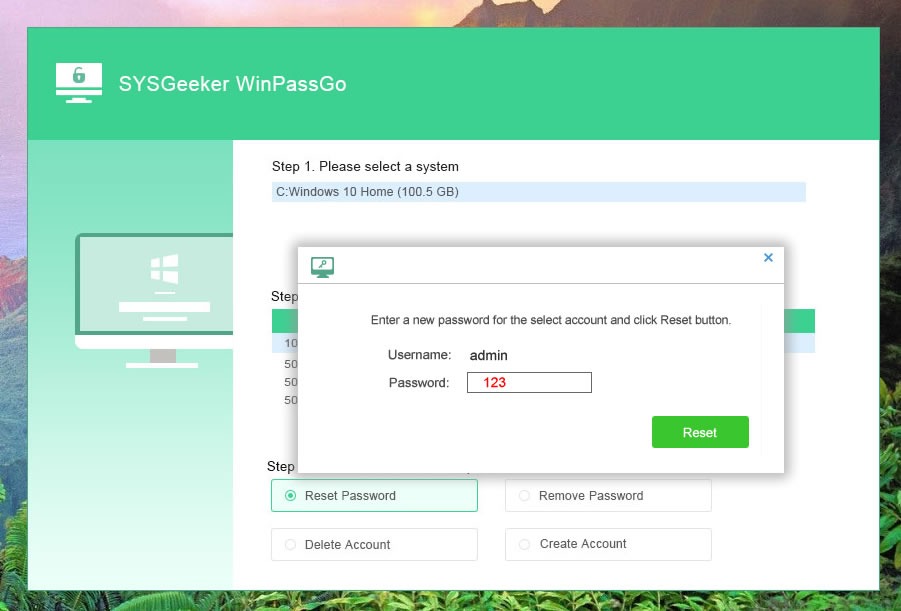
The core of WinPassGo is that it is flexibly compatible with both UEFI and MRB computers, which is not supported by many other softwares, this is especially significant for those computers with UEFI boot mode. In our test, it took only 3 minutes to remove a 9-digit password from a Windows 10 computer. This is incredible! In addition to removing the password, you’re allowed to reset a new password for exiting accounts, create new account and delete old account.
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
|
John the Reipper is an open source password recovery tool available for free which uses a special method to recover the Windows password. However, it is this method that makes this tool extremely slow to use. It cannot recover passwords which are more than 8 characters in length because of this slowness, recovering those passwords may take months, even years. John the Ripper also does not feature a GUI version. So if you have not used a command prompt before, or is not comfortable using utilities that does not have a GUI, this tool may not be suitable for your use.
The free version of John the Ripper will only provide you with the raw code, you will need to create the program from that raw code before you can use it. That renders it useless for people who are not that technically sound. There is a paid version available which gives you the actual software, however, that supports only Linux and MacOS.
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● It is not GUI based, you ned to executed from the command line. ● Some features are not free! ● It hasn't been updated for a long time. |
This would be one of the best, and easiest tools to reset your lost Windows passwords. It supports almost all major versions of Windows including Windows Server line of OS. It can help you to remove passwords for both local user and Admin accounts, and domain accounts.
Like other tools, this program provides two ways to create a windows password reset disk, USB and CD/DVD. If your computer doesn't have a built-in CD-ROM drive, then USB is a good option. iSeePassword Windows Password Recovery Pro provides users with 2 different version: Pro version and Advanced version. Pro version. They can all easily remove admin password from Windows. The only difference between them is Pro version only can remove the forgotten password, it can’t reset the new password and create new account. And the advanced version can do this all. In fact, the Pro version already meets most users' needs, as once you can access you system, you can add or remove accounts in Settings.
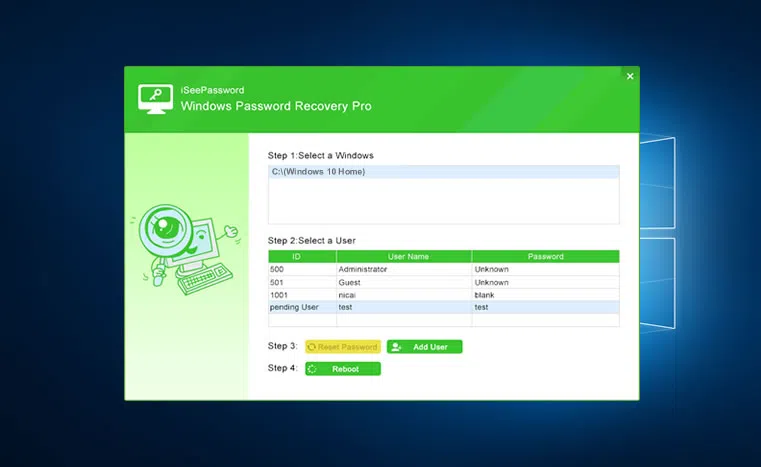
This utility is compatible with both Windows and MacOS, so in case you do not have another Windows PC available to create the bootable media, you can use a Mac instead
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Doesn’t support resetting Microsoft account. ● Doesn’t support domain password. |
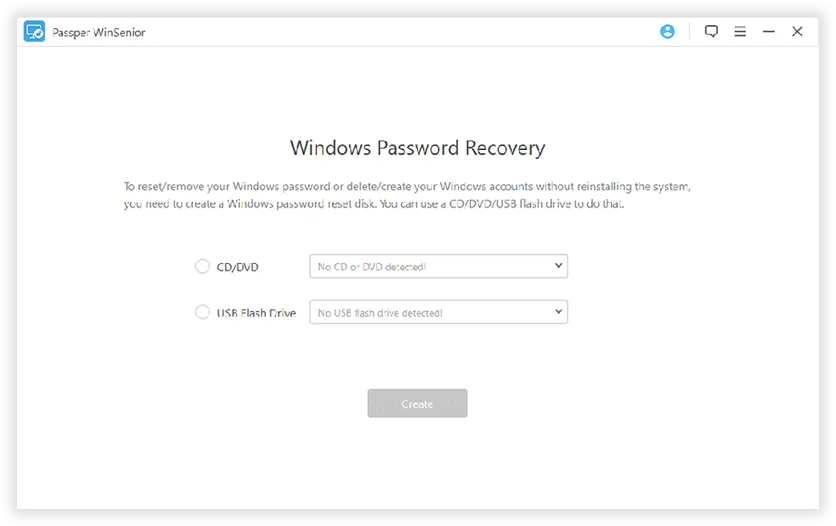
This is a paid tool available for resetting Windows passwords. But it can do more than just recover passwords. For example, it can help you delete or create new Windows user accounts. Passper WinSenior has a restricted free version available. But for full functionality, you need to purchase it and seems to be a bit too costly. There are various purchasing options available. It supports almost all modern versions of Windows OS including tablets running Windows OS. Also, it is pretty small in size (< 200 MB).
PassPer WinSenior doesn’t split the product into several versions, instead, it introduced 4 different pricing strategies. You can choose to pay monthly, yearly, or purchase a one-time lifetime plan and the cheapest plan is $29.95 monthly, which I think it's too expensive. The usage methods are actually the same, you also need to create a password reset disk from USB or DVD/CD on another working computer, then connect it to your locked PC and let it boots from the password reset disk, then your computer will boot from the USB or DVD/CD and shows the accounts you created before.
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Paid software is very costly. ● Some features are not free! ● It hasn't been updated for a long time. |
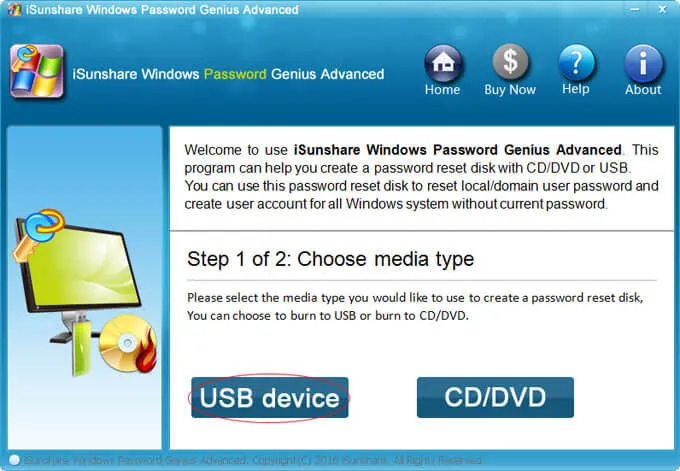
Unlike some of the previous tools we discussed, the iSunshare Windows Password Genius is a GUI based tool, and has a user-friendly user interface. It has a free version available, with limited functionality of course. If you want to avail the premium features, which is what you would need mostly, you need to pay for it. This tool also can help you reset or remove the forgotten administrator/user password from All Windows Edition as well as Microsoft accounts, But in our test, we didn’t success in resetting Microsoft account password with this tool.
It's also easy to use, all you need to do is install the software and create a bootable media, then wait this tool to do its magic. It does come with a 96.5 percent success rate guarantee. Has free tech support available, in case you face any issues. Coming to issues, it can be quite frustrating to use with all the errors that comes up during burning of the media, or detecting the USB drive.
This tool comes out with 4 editions (Standard, Professional, Advanced and Raid) and each version has a different function. In fact, the standard edition is capable of meeting basic password reset requirements.
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Free version has limited functionality and you would almost definitely need the paid version. ● Throws errors every now and then. ● Doesn't work on 64-bit operating system. |
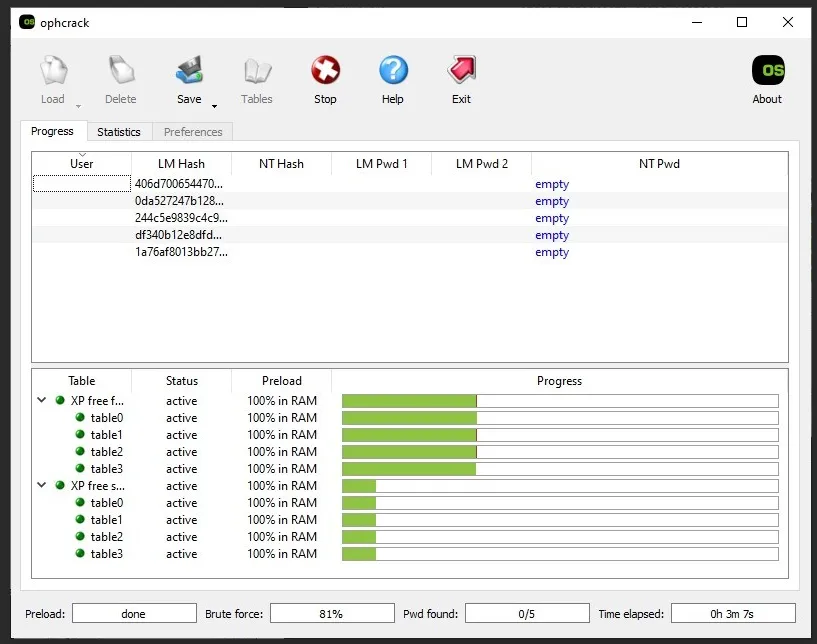
Ophcrack has always been considered as one of the all-time popular password recovery tools since it it uses a special algorithm called rainbow tables. Ophcrack is a completely free utility that can hack into the Windows password tables to recover the passwords for local accounts. It is different from the general Brute-force cracking tools, it doesn’t try thousands of combinations of letters, numbers and special characters each second. Conversely, the Rainbow tables pre-computes the hashes used by passwords, then ,by comparing the hashes it has, it can locate the password quickly. Ophcrack is complicated to use and not suitable for the computer novice, you need to install the the third-party tools like pwdump or fgdump, which is used for extract the SAM of a Windows system.
The free Rainbow tables can be download in its official website, but only XP and Vista rainbow tables are free. If you want to crack the password for Windows 7 and Windows 10, you need to purchase the corresponding rainbow tables from Objectif Securite.
Ophcrack password recovery tool supports most major versions of Windows including 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP, and 2000. It has both GUI and command line version, the later being targeted towards advanced users. Ophcrack is not malware, but the tool (pwdump) to access the SAM may be flagged and quarantined as malware by many virus scanner.
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Hasn't been updated since 2013. |
The Offline NT Password & Registry Editor is another open source Windows password recovery tool which is available for free. However, it is quite different from Ophcrack in that it erases the existing password instead of recovering it, along with giving you the ability to set a new password for your account. Its usage is similar to that of Ophcrack in that it creates a bootable USB or CD/DVD using which you can boot to your computer to erase password, or set the new password. However, unlike Ophcrack, the Offline NT Password & Registry Editor is a command line tool and does not have a GUI, so new users might find it difficult to use since the process of erasing the password is quite complex.
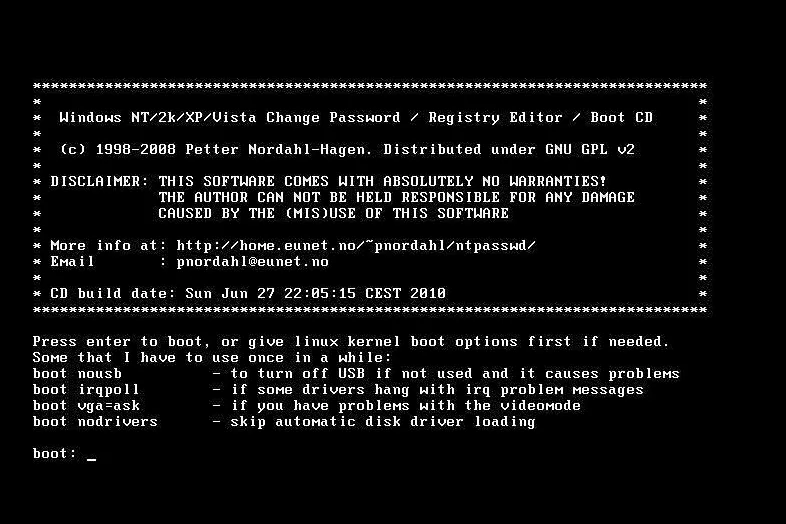
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Entirely text-based or command based tool. |
PCunlocker is yet another paid tool for resetting windows lost password, we included it in our list because it has a success rate of 94.6% when it comes to resetting passwords on our Windows 7 Home, 64-bit computer. According to its advertising description, it works for all kind of accounts password including Microsoft password, domain password and local account password. But in our tests, the domain password was not reset successfully, I don’t know why, is it my operation problem? PCUnlocker is compatible with all Windows Editions including Windows 7/8/10 and Windows server, so, don't worry about compatibility. But one thing to note is that you have to download and install additional software called ISO1Disc, which is used to create a bootable USB to run the PCUnlocker program, once you installed this tool on your computer, click Browse button to load the PCunlocker.iso then it starts to write the PCunlocker tool to your USB drive or DVD/CD. Compared to other tools, Tit takes more detours.
Like other paid softwares, it also offers a money-back guarantee in case you have failed to reset your password with this software. Each edition has its own purchase plan, you can buy the version for just $19.95 varying based on the plan you select.
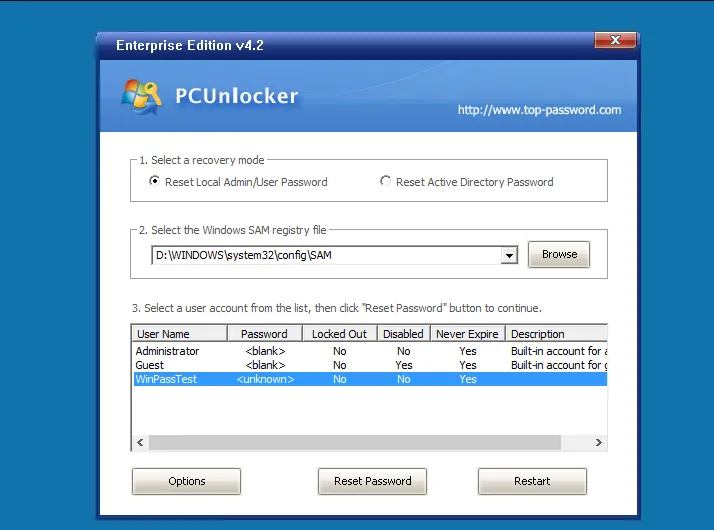
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Requre additional ISO burning tool. |
Lazesoft Recover My Password is another free Windows password recovery tool that you can use to recover Windows forgotten admin password as well as other local account password. There is no essential difference from the previous Windows password recovery tools, it also removes your account’s password instead of recovering it, you’re allowed to remove the password entirely, reset it to blank or new one, enable, unlock or disable user accounts. To start using Windows Password Reset Standard, just download an ISO file, mount it, and start resetting your password. Learn how to use ISO files from our guide. Lazesoft Recovery My Password provides a graphical interface for creating a bootable reset disk, and may be more appropriate for new users.
Lazesoft claims that it has 100% recovery rate when removing password for Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7, 8 and even Windows 10. However, in our test, we didn’t succeed in a Windows 10 Professional Edition. But their after-sale service is timely enough to reply and help us. So if you get stuck in using their product, you can check out its comprehensive FAQ or contact them by email.
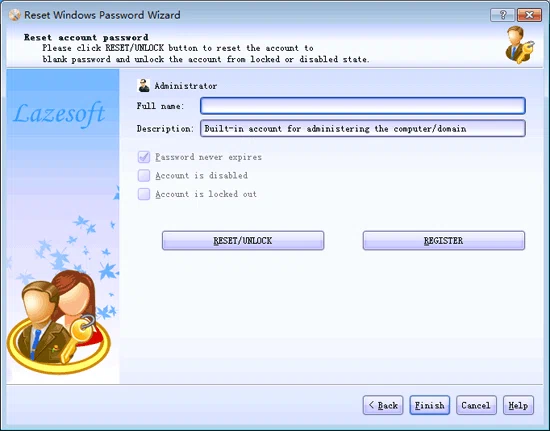
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Requre additional ISO burning tool. |
LCP Windows Password Cracker is yet another free tool for recovering Windows NT/2000/XP/2003 password. It also uses the password hashes stored inside Windows to recover the passwords, but it could import hashes from local and remote computers in SAM. It’s a real brute-force cracking tool and comes with multiple attack types including dictionary attack, brute force attack, or a hybrid attack. I don’t suggest you to try this tool on a Windows 10 computer, as it will consume the majority of your machine resource..
Although it has been updated, unlike the Offline NT Password & Registry Editor, it is quite cryptic to use, especially for people who are not that technically sound. For example, it would ask you to locate the password file if it is not found in the default /Config sub-directory on your Windows installation. If you don’t know what that is, I would suggest you to avoid using this tool because then you might end up causing more harm to your system.
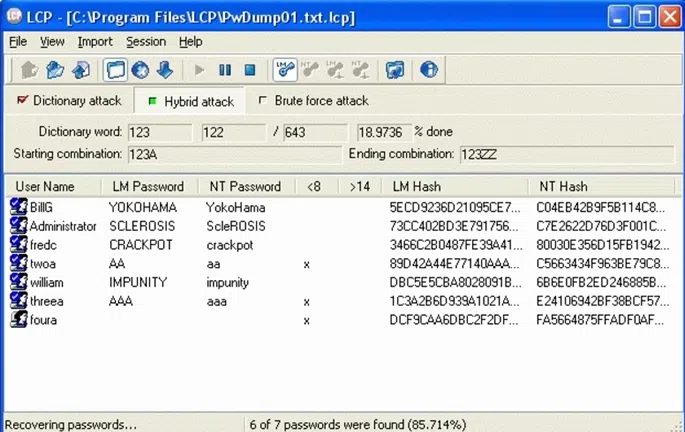
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Requre additional ISO burning tool. |
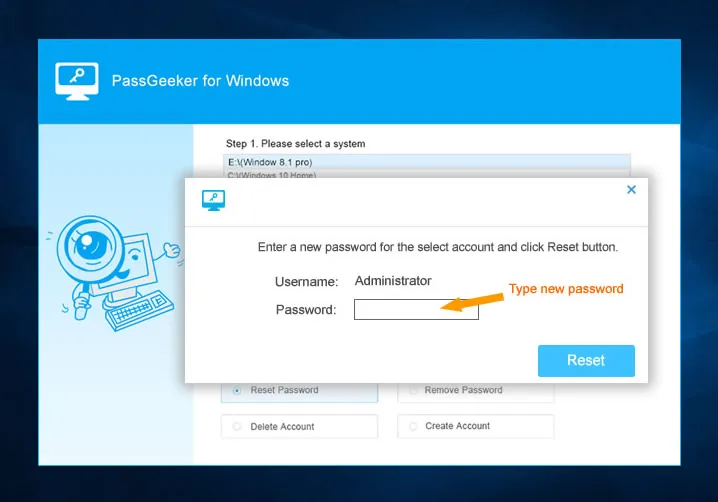
The last one I would recommend is PassGeeker for Windows tool, it is said that it’s a leading developer of password recovery software with a success rate of about 98.5%, so I downloaded it and test it with great interest. Just like other softwares, it also created a password reset disk from USB drive and DVD/CD, but what surprised me was its burning speed, it only took 30 seconds to write the ISO image to a USB drive, you know, this is not possible with other softwares, then connect it my test PC (HP laptop with Windows 10 Home, 64-bit, UEIF boot ), it can boot smoothly from USB drive and shows all the registered accounts, then it allows me to reset a new password for admin account.
In our test, PassGeeker for Windows tool not only can reset or remove Windows lost password form Windows 10,8,7 and Windows server R2, but also it won’t touch the original data during the password recovery process. Again, it provides three license plan, Basic, Family and Business plan, choose the right solution for your needs, but I recommend to select the Family place since it can reset 8 PCs. Also it offers free update lifetime, if you get stuck, contact them by email.
| Pros: | Cons: |
|---|---|
|
● Requre additional ISO burning tool. |
| Items |
Support OS |
Difficulty |
Time Used |
Compatibility |
Cost |
Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | High difficulty( No GUI) | Hours or Days | Windows and Linux | Free | 58.9% | |
| All | High difficulty( No GUI) | Hours or days | Win, Mac or Linux | Free | 47.3% or Lower | |
| All | Very Easy (GUI) | 3 - 5 Minutes | Windows and Mac | Paid | 99.2% | |
| All | Easy | 10 - 15 Minutes | Windows | Expensive | 87.6% | |
| All | High difficulty( No GUI) | Hours or Days | Windows | Free and Paid | 68.4% or Lower | |
| All | Very Easy (GUI) | 5 - 10 Minutes | Windows | Paid | 98.6% | |
| All | Easy | 20 Minutes | Windows | Paid | 81% | |
| All | Medium Easy | 30 minutes | Windows | Paid | 78.3% | |
| All | Difficulty (No GUI) | Days | Windows and Linux | Free | 39.6% | |
| All | Easy (GUI) | 3 - 5 Minutes | Windows and Mac | Paid | 97.5% | |
| All | Easy | 15-20 Minutes | Win, Mac and Android | Paid | 79.3% |
We know there are many different types of Windows password recovery tools available online, but we only selected the best paid or free tools for review. If you read the article carefully, you will find all of these tools are different in terms of power, usability, prices, recovery methods and compatibility.
We actually downloaded and installed each software on our computer and test its functions, easy of use and others to make sure our our reviews are authentic. You can choose the right tools based on this reviews.
Success rate is the first factor you must consider, because it directly affects the outcome. Here, we recommend choosing iSeePassword, WinPassGo, Passper WinSenior, PassGeeker for Widnows and PCunlocker, all of them has the high success rate of resetting Windows password. The software difficulty is also one of the important factors that need to be considered when we choose a Windows password reset tool, because some Windows password recovery tools are command based utilities that don’t come with user graphical interface. It's complicated to use and error prone. Such as Ophcrack, John the Ripper and Offline NT Password & Registry Editor. When we forgot our Windows password, we need to access to our system urgently and quickly. However, some Windows password reset tools will take a long time to reset a password, this because the algorithms and principles are different. So, we recommend selecting a software that can create a password reset disk. Such as: WinPassGo, iSeePassword, PCunlocker and PassGeeker for Widnows. We know, to reset your forgotten Windows password, you have to create a password reset disk on another working computer. However, most people don’t have a Windows device available in most cases, but if you have a Mac, Linux or Android device, then you still be able to reset your password. So, a tool that supports multiple platforms will be your first choice. Recommend: iSeePassword Windows Password Recovery Pro and iSunshare Windows Password Genius. In this list, some of the Windows Password Recovery tools are free and some are for a fee. But in our test, freeware like Ophcrack is not ideal, it’s complex to use, time-consuming and no after-sale support. So, I highly recommend to choose paid software, professional and guaranteed. |
This is the most concerned issue for the users who plan to use Windows Password Recovery Tool. After more then 56 tests, we firmly believe that your data and files on desktop or hard drive will never be erased or lost when you try to reset password, but the premise is that you must use the professional Windows password reset tool.
Why do say that? Because the software with WinPE will be burned into USB or DVD/CD, and your system will boot from USB drive, DVD/CD, all the operation will be finished in the WinPE environment. It means it will never touch your data and files.
In this list, all softwares can be able to find your lost Windows password or remove it completely, just the time and ease of use are different. All these tools are different in terms of power, recovery methods, usability, compatibility, success rate, price, and more, you can pick up a tool based on your needs. I personally prefer to go with paid and professional Windows Password Reset tools, because save time and worry.
In order to avoid situations where you forgot your Windows password, we recommend you to use a good password manager or note down somewhere.
 Sit tight and read with full attention while we tell you exactly what to do recover Windows 10 password without losing data.
Sit tight and read with full attention while we tell you exactly what to do recover Windows 10 password without losing data.  Well we understand how you forgot Windows 10 password in all your categorical conditions, and along with empathy, we would present three best solutions to overthrow the situation.
Well we understand how you forgot Windows 10 password in all your categorical conditions, and along with empathy, we would present three best solutions to overthrow the situation.